Mixtures Unit Test - Study Hints
*The test is on Thursday, April 12
*If you are absent due to illness or athletics it is your responsibility to arrange a make-up date with Mr. Mak as soon as possible
-What is matter? What are its two key properties?
-Main ideas of the particle theory
-Classification of matter into pure substances - elements and compounds
-Classification of matter into mixtures - homogeneous (solutions) and mechanical mixtures (heterogeneous)
-Explain the difference between solute and solvent
-Three ways to increase the rate of dissolving and why they work
-Prove, using simple calculations, why smaller particles have increased surface area (see image below)
-Explain the difference between dilute vs. concentrated solutions
-Explain the difference between soluble vs. insoluble
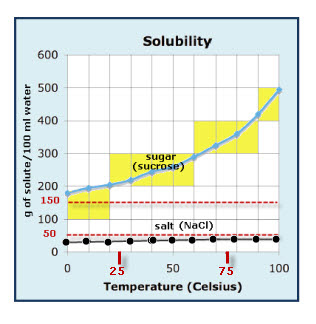
-Concentration of a solution (Xg/100ml)
-How to read a solubility graph (the one we discussed in class is posted above)
-Explain the difference between unsaturated vs. saturated vs. supersaturated solutions
-Explain how Rock Candy forms
*If you are absent due to illness or athletics it is your responsibility to arrange a make-up date with Mr. Mak as soon as possible
-What is matter? What are its two key properties?
-Main ideas of the particle theory
-Classification of matter into pure substances - elements and compounds
-Classification of matter into mixtures - homogeneous (solutions) and mechanical mixtures (heterogeneous)
-Explain the difference between solute and solvent
-Three ways to increase the rate of dissolving and why they work
-Prove, using simple calculations, why smaller particles have increased surface area (see image below)
-Explain the difference between dilute vs. concentrated solutions
-Explain the difference between soluble vs. insoluble
-Concentration of a solution (Xg/100ml)
-How to read a solubility graph (the one we discussed in class is posted above)
-Explain the difference between unsaturated vs. saturated vs. supersaturated solutions
-Explain how Rock Candy forms